Software Design
The dueling robot uses a set of tasks to run and target an opponent succesfully. The robot uses MicroPython to control two motors and adjust the pitch and yaw axis in order to follow the target found in the provided thermal camera. Once the target is located and tracked, the motor engages the flywheels and servo motor to propel a dart forward.
main file

The main.py file uses a task management file to manage the yaw, pitch, camera and firing tasks. The task diagram of the file is above, and its contained tasks are detailed below.
main - Master Task

The master task shares the current turret status with all other tasks. When the master task is initilized it moves into it's state 1, where it sends the pitch and yaw motors to move to their initial positions. It next waits until 4.9 seconds, in which it will then send a signal to the motors to begin following the target based on the position data sent by the camera task, and for the flywheels to begin spinning up. Once 5 seconds has been reached, if the yaw and pitch motors are both on target, fire the dart by articulating the servo motor. Once the ten second firing window passes, powerdown the flywheels and send the yaw motor back to its starting position. The FSM for the task is above.
main - Yaw Task
The yaw task takes the current horizontal position and uses the control loop developed in lab 2 to try to aim at the target. If Yaw Task is at the same position as the target, then the target is located in the horizontal axis and the Yaw Task shares Y_OnTarg to high to the Firing Task.
main - Pitch Task
The pitch task takes the current vertical position and uses the control loop developed in lab 2 to try to aim at the target. If Pitch Task is at the same position of the target, then the target is located in the vertical axis and the Pitch Task shares P_OnTarg to high to the Firing Task.
main - Camera Task
The camera task queues the location of the target in its field of view with both the Yaw Axis Controller and the Pitch Axis Controller. It utilizes a an algorithm that 'splits' the 32 by 24 pixel grid into an 8 by 24 grid of 'arrays' (effectively splits them as so, but not technically). It then compares the average heat value of each split array to find the maximum and returns its x and y location relative to the center axis of the screen.
main - Firing Task
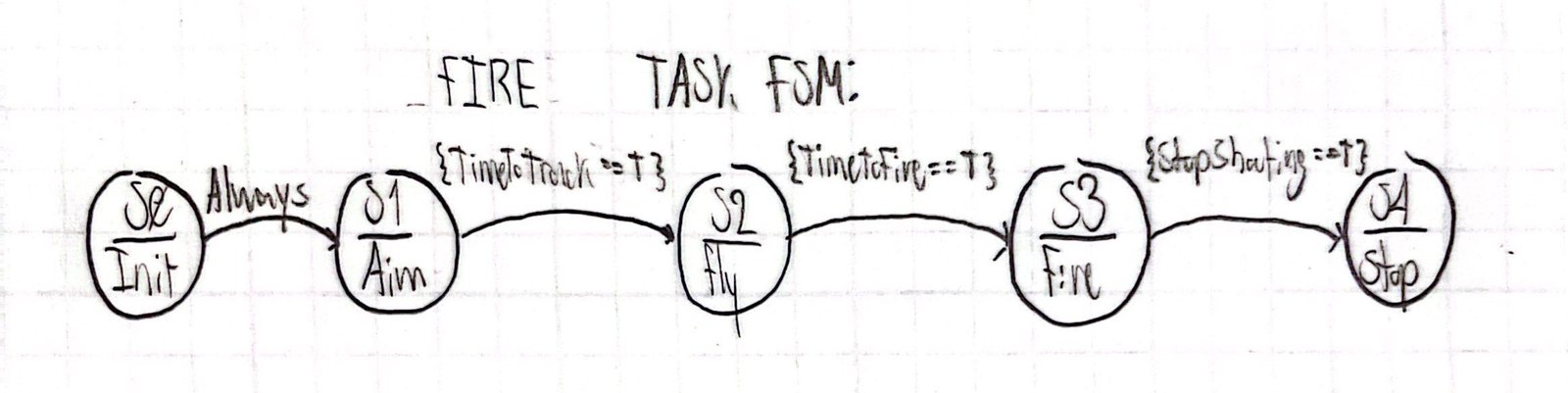
The firing task takes the data shared by both the Yaw Task and the Pitch Task in the form of the two booleans: Y_OnTarg and P_On_Targ respectively. If both booleans are True then the firing task commands the servo motor to articulate a dart into the rotating flywheels. The FSM for this task is above.
mlx_cam file
The mlx_cam.py file is used to take images through the provided IR camera. This file then returns the x and y components of the target.
motor_driver file
The motor_driver.py file manages the PWM signal sent to the provided motor in order to position the motor at the desired location.
encoder_reader file
The encoder_reader.py file reads and tracks the inputed motor's encoder and returns the value.
closed_loop_control file
The closed_loop_control.py file uses runs a closed loop controller on the inputed motor to assist in positioning the motor.
cotask file
The cotask.py file is one of the two behind the scenes task management files which assist main.py in running. It specifically assists with helping tasks run after each other.
task_share file
The task_share.py file is one of the two behind the scenes task management files which assist main.py in running. It specifically assists with sharing data with each task.
